
Introduction: Why Are Airplane Windows Round?
If you have ever looked outside your seat during a flight, you’ve probably noticed that airplane windows are round. It might seem like a simple design choice, but there’s a surprising amount of science, safety engineering, and aviation history behind this shape. In this article, you’ll learn why airplane windows round designs became the global standard—and why square windows are dangerous.
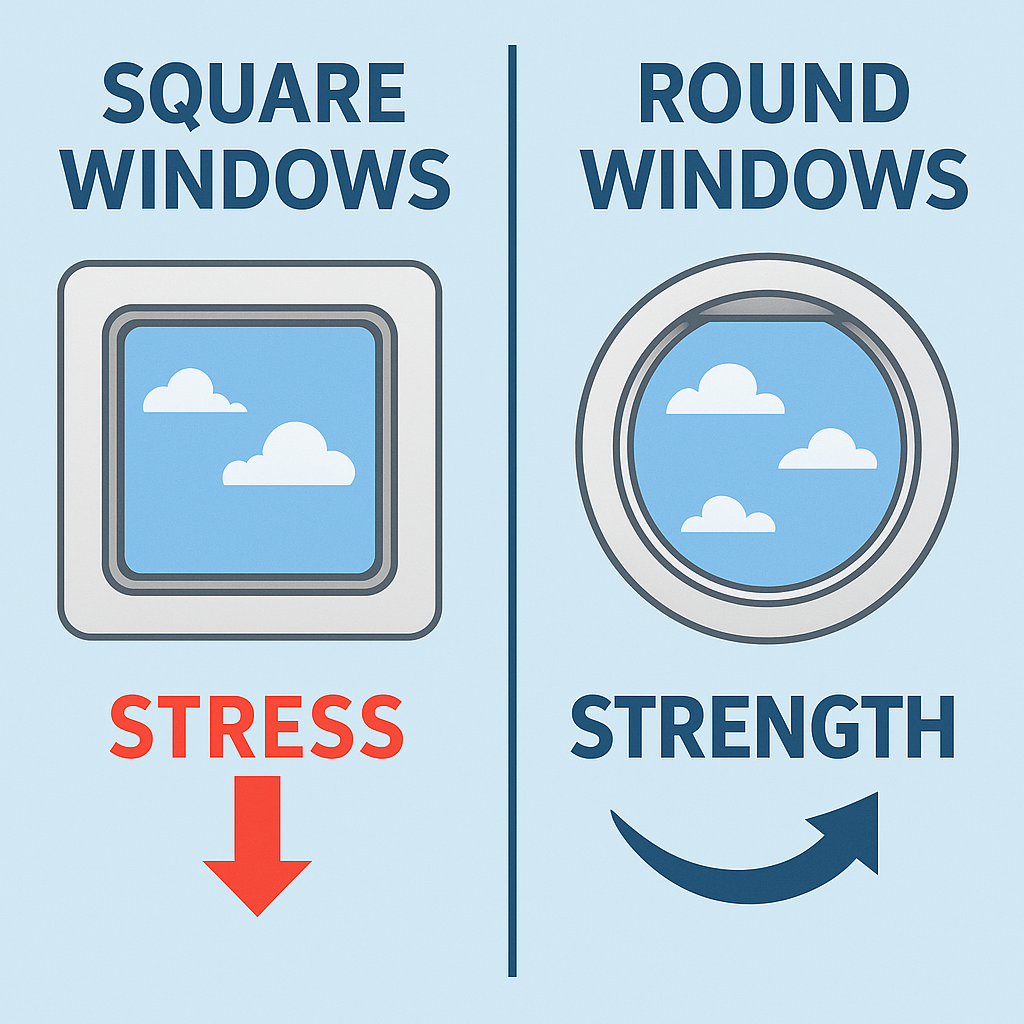
1. Round Windows Prevent Dangerous Structural Stress
One of the biggest reasons airplane windows are round is stress distribution. When a plane climbs thousands of feet, the cabin becomes pressurized. Round shapes spread pressure evenly, while square windows create stress points at the corners.
In the 1950s, engineers discovered that square windows caused cracks during flights. The round airplane windows we see today eliminate these weak points and make the aircraft far safer.
2. The Comet Disaster Changed Window Design Forever
In the early days of commercial aviation, airplanes had rectangular windows. This design led to several catastrophic failures on the de Havilland Comet. During flight, cracks formed at the corners of the square windows, eventually causing the aircraft to break apart.
These accidents changed aviation forever. After years of investigation, engineers learned that airplane windows round designs dramatically reduced stress concentration.
From that point on, every commercial aircraft adopted round or oval windows.
3. Round Windows Handle High Altitude Pressure Better
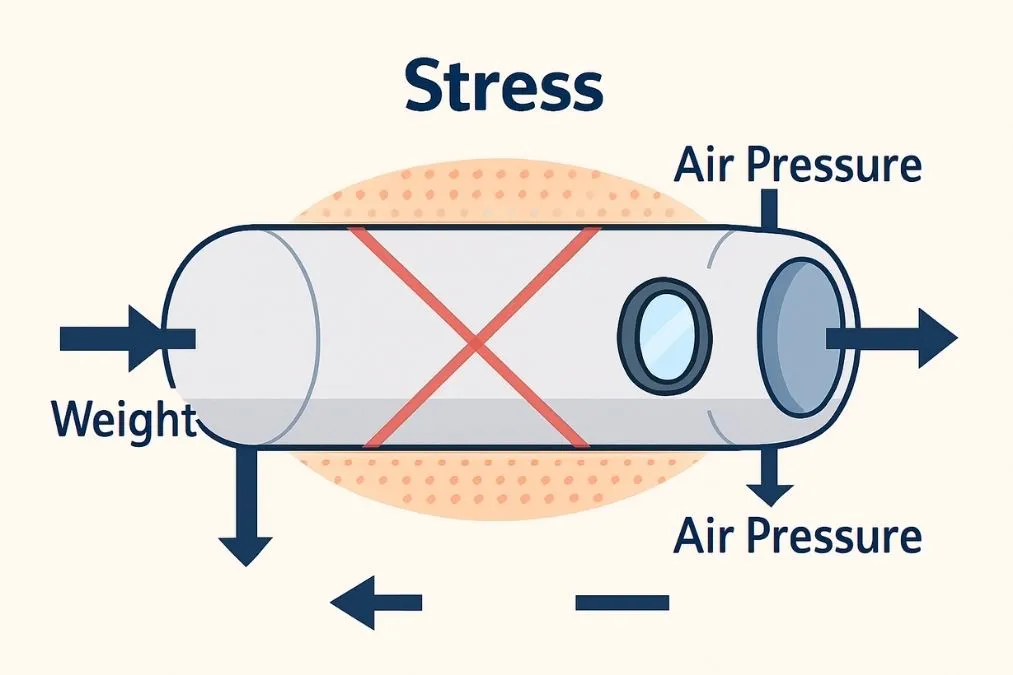
As airplanes reach cruising altitude, external pressure drops while cabin pressure is maintained. This creates a strong outward force against the fuselage.
A round window:
- bends stress evenly
- has no sharp edges
- resists deformation
- stays stronger over time
This is why nearly all modern aircraft use round or oval-shaped windows, not square ones.
4. They Reduce the Risk of Metal Fatigue
Over years of flying, airplanes experience pressure cycles—every takeoff and landing causes the cabin to depressurize and pressurize again. Sharp corners react poorly to repeated stress.
Round airplane windows reduce metal fatigue around the fuselage because the load is distributed evenly. This results in:
- fewer cracks
- longer aircraft lifespan
- safer flights
5. Passengers See Better Through Round Windows
There’s also a practical benefit for passengers: round or oval windows improve visibility. The curved edges reduce internal glare and framing distortion, giving you a clearer view of the sky.
It’s a small detail, but it enhances the passenger experience during the flight.
6. Round Windows Make the Cabin Look More Spacious
Designers discovered another advantage: ovals appear more elegant and open. Round airplane windows help break the monotony of the fuselage interior, making the cabin feel more modern and visually balanced.
This is why premium cabins often have larger, smoother window frames.
7. Modern Planes Combine Both Engineering and Style
Today’s airplane windows round designs are the result of decades of research. While safety is the primary reason, designers also consider:
- passenger comfort
- noise reduction
- aesthetics
- safety regulations
- fuel efficiency (smaller windows make the fuselage stronger)
Everything about a modern round window is optimized for performance and safety.
Conclusion: Why Airplane Windows Round Shapes Matter
The next time you look out of an airplane window, remember that its round design is not accidental. It’s a lifesaving engineering decision shaped by history, physics, and major aviation innovations.
Round airplane windows help planes:
- resist pressure
- avoid cracks
- improve safety
- enhance passenger experience
Now you know the fascinating truth behind one of aviation’s most iconic features.
Sources:
- UK Air Accidents Investigation Branch (AAIB) – Official investigations
- Aviation Safety Network – de Havilland Comet accident database
Further reading (technical):

